


Technical terms
The minimum temperature at which the generated flammable vapor gets inflamed.
When an ignition source (fire, spark, etc.) gets close at this temperature, it ignites and burns.
Upon application, it forms an oil-repellent layer and prevents the entrance, leak and raise of oil, grease, solder, flux, etc. It also has water repelling effect.
It is a kind of synthetic oil.
It is resistant against cold temperature and gives supreme lubrication against metals but may cause cracks and swelling on some resins and rubbers.
It is mainly used in pressure bearings and infiltration bearings.
Antifriction is reducing of friction and abrasion, and is one of the functions required for lubricants.
The oil is used as a base for lubrication oil and grease, with no additives in it yet. It is categorized into mineral oil and synthetic oil. For grease, mineral oil is commonly used but under special condition in which mineral oil cannot satisfy the requirement, a variety of synthetic oils are used. Base oil has a lot to do with lubrication, heat resistance, stability against oxidation and resistance against low temperature, rubbers and resins.
Grease is a type of lubricant that comes in paste (semisolid) format made of liquid lubrication oil (base oil) and puffing agent dispersed in it. Additives are also mixed to give function according to the purpose of the use.
Solid lubricant is a substance used to prevent damage of the surface in relative motion or to reduce friction and abrasion. Unlike liquid lubricants such as lubrication oil, it is less likely to cause direct contact of materials on the friction surface. While liquid lubrication tends to cause galling with oil layer damaged by heavy load or slow movement, solid lubricants form a solid layer on the surface, preventing direct contact of the materials when used properly. Many solid lubricants are in layers or have shear strength if not in layered structure to add lubrication effect. Molybdenum disulfide, graphite and mica are the former, and fluorine resin and soft metals such as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) are the latter.
The bearing has rolling elements between the shaft and its supporting structure and changes sliding contact to rolling contact to reduce friction. Ball bearing uses balls and roller bearing uses rollers as rolling elements. Coefficient of friction is lower for rolling than sliding at activation, and rolling bearing outperforms slid bearing in assembly and maintenance perspective. Grease is usually used for its lubrication.
Cameras are required to move quickly and accurately under various conditions from low temperature to high temperature and humidity environment.
Oil leak is not acceptable around lens and shatter.
DRYSURF, our quick-drying lubricant, is frequently used to fulfill these multiple requirements.
A mixture of hydrocarbon compounds from underground such as oil (crude), gas, coals or even impurities. In general, the crude derived oil is commonly used in industrial goods.
The amount (in mg) of potassium hydroxide (KOH) needed to neutralize all acidic compounds in 1g of a sample. With lubricants, it is sometimes used to check the level of degradation or foreign material contamination. The measurement method is specified in JIS K 2501.
The bearing consists of pressed metal powder whose pores made in manufacturing process are impregnated with a lubricant. When operating, the lubrication oil comes out from the pores by pumping effect of rotation, and when stopped, the oil goes back to the pores with capillary action.
Puffing agent keeps oil in grease format.
Its content volume and type affect various parameters such as heat resistance, water resistance and hardness of the grease.
It is the amount lost with evaporation when grease is exposed to high temperature. The amount is mostly subject to the loss of base oil, which is impacted by the type of base oil and its molecular weight. If evaporation amount is large under high temperature, it could result in hardening of grease, insufficient lubrication and shorter lubrication effect, so it is one of the evaluation points for heat resistance of grease.
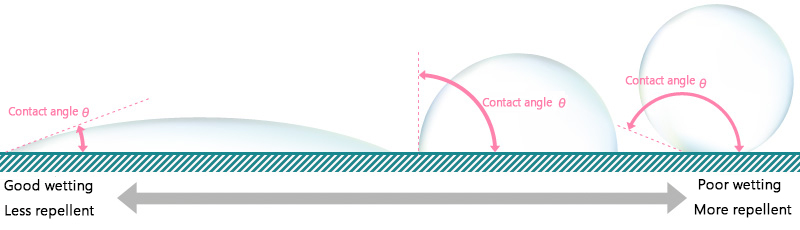
Contact angle, shown below as θ, takes a value between 0° and 180°. The dot line shows the tangent line at the liquid droplet outline and its intersection with the solid surface.
Solvent crack is a small line caused by solvent touching the surface of resin molds. Solvent here includes not only chemicals such as alcohol but also everyday products including oil, wax and cosmetics.
Insulation resistance is a value that shows the degree of resistance between insulated conductors. It can be found, for example, on the cover of electrical cables. It is measured in MΩ (mega ohm). When the insulation resistance is low, it could cause electric leakage, causing a shock or fire.
When electricity flows in two conductors touching each other, the voltage drops and the temperature goes up at the contact point. This is due to contact resistance, and its value is influenced by the kind of conductors, pressure, the presence or absence of oxide film, the status of absorbed gas, current density, etc.
The grease is used to protect contact points and lubricate the slide contacts and connectors. Very strict foreign material control is required to prevent malfunctions at contact points.
The quick-drying lubricant comes in liquid format, and is a lubrication agent dispersed in fluorine solvent. As fluorine solvent is highly volatile, a thin and uniform coating layer is formed instantly. Compared to grease, it causes little scattering, running or staining and is also easier to handle. Semi-dry type contains oil and has slightly wet feeling, while completely dry type has no oil content and feels dry.
Dielectric breakdown is the loss of insulating function of an insulator resulting in current flow, caused by voltage going beyond the limit. The voltage at the point is called dielectric breakdown voltage, and dielectric strengths is the voltage divided by the thickness of the material. It is measured in kV/mm, and the value is assigned for each substance, but the value goes down when air bubbles come in or moisture is trapped by the material. It is ideal to have insulators with large dielectric breakdown.
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is the analysis of chemical bonding information by irradiating infrared lays to the subject and causing spectral diffraction of transmitted (or reflected) light. It is supplementary used to understand the molecular structure or status of the subject material.
The sliding surface supports the shaft in slide bearing. Oil is mainly used for its lubrication, but as it requires complex oil supply / sealing device, grease is sometimes used to simplify the device.
It shows the hardness of grease with a number which is ten times the depths (in mm) of the measurement cone entering into grease after 5 seconds. The smaller the value, the harder the grease.

It is the temperature at which the first droplet falls when the substance, heated in test condition using standard device, changes from semisolid to liquid.
Additive is mixed to improve physical and chemical property of the grease. Some additives have multiple functions, while others cause negative impact on other functions.
It is obtained by the time it takes (in seconds) for the certain amount of liquid at defined temperature to naturally flow down the capillary of the viscometer multiplied by the constant of viscometer. Kinematic viscosity shows the viscosity of oil, and the greater the value, the more viscous the oil.

Low molecular siloxane inside silicone oil and grease may volatilize after the product is manufactured. While the boiling point is high for low molecular siloxane, it is highly volatile and could turn into steam and disperse in the air even at room temperature or body temperature. It is known to cause malfunctioning, breakdown and problems at electric circuits, relay contact points and semiconductor manufacturing lines.
The test checks the corrosion caused by the oxide created with acidic substance or oxidation degradation, or by corrosive sulfur. After applying the grease on or soaking a piece of polished copper in it, the degree of degradation and discoloring is assessed for the copper piece and grease.
Unstable signal produced for some reason when contact points touch each other, causing malfunction of electronics. When normal grease is used at low temperature, it tends to get solid, disturbing the contact points to cause chattering. Fluorine lubricants durable against low temperature are often used in those places.
Image quality of optical instruments could be lost by micro dust inside the body tube or around the image sensor, and this product is to remove such dust. It is especially useful for capturing dust that could not be removed even in a clean room.
Viscosity is the degree of stickiness of a liquid, and it is also referred to as viscosity coefficient.
It shows the temperature reliability of the viscosity of lubricants, and the greater the value, the smaller the fluctuation of viscosity by temperature. The coefficient is calculated using kinematic viscosity at 40℃ and 100℃.。
Corrosion inhibitor is an additive that prevents corrosion of the metal surface with acidic substances or corrosive gas such as sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere. An example would be nitrogenous compounds such as benzotriazole.
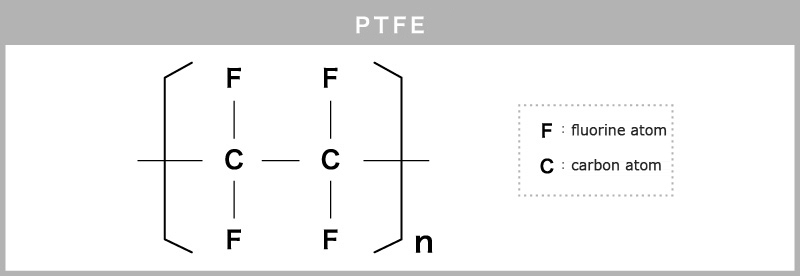
It is the polymer with smallest friction coefficient, which is believed to be due to weak cohesive power.
Density is the quantity of mass per unit volume. 。It is measured in g/cm3 (gram per cubic centimeter).
Boiling point is the temperature at which the saturation vapor temperature of a liquid equates to external pressure.
Fluorinated grease is made of fluorine oil as base oil and PTFE as puffing agent. Compared to synthetic oil, it is superior in load resistance, evaporation amount and water repellence, it lasts longer without degradation and does not damage resin and rubber with low oil resistance such as polycarbonate and acryl. With its wide range of application temperature, resistance against chemicals, insulation performance, incombustibility and high viscosity coefficiency, it is used as lubricant in painting line under an atmosphere of the solution, in clean rooms, high vacuum devices and for permanent enclosure.
Polyalphaolefin, or PAO, is a polymer made by polymerizing alphaolefin. It is widely used as hydrocarbon synthetic lubricating oil.
Friction coefficient μ is the frictional force F divided by normal force N to the contact surface in dimensionless quantity (μ=F/N), and is measurable with friction test machine. In general, moving friction coefficient is larger than static friction coefficient. When the maximum static friction is reached, the object starts to move.
Solvent is the liquid in which a solute is dissolved, and it is used to make other materials easier to use. Organic solvents are commonly used but their combustibility and impact on resin are concerned. Meanwhile, our DRYSURF mainly uses fluorine solvent which is incombustible and has little impact on resin.
Organic molybdenum is added to grease as extreme-pressure agent. Grease with organic molybdenum is especially effective for lubrication of metal sliding parts. Also unlike molybdenum disulfide, it is not black and causes little black stains upon application.
Our major product: HI-LUBE MG-2395
It is a parameter of liquid fluidity at low temperature, used in oil and lubrication industry. The temperature is slightly higher than the point at which the liquid freezes.
It is a parameter to assess the oil separation tendency of a grease under static condition. The greater the oil separation of the grease, the more unstable it is in storage and therefore is not suitable for long term use in bearings etc. Certain degree of oil separation, however, improves its effectiveness.

Copper and silver are useful for contact points of electronics due to their easiness of soldering and superior electric properties such as electrical resistance. Sulfuration of copper and silver would have negative impact on those properties; therefore, contact grease to be used with those materials should include additives to prevent sulfuration and protect the contact points.
Fluid bearing is used in motors etc. and supports the smooth movement with fluid filling such as air or liquid in the gap of bearings. Instead of the bearing ball and lubricating oil usually applied to the gap between the rotating shaft and bearing of a motor (ball bearing), fluid bearing uses oil and air to realize smooth movement.


























